The renaissance of natural fibers: God's Forgotten Gift 2021-09-21 10:57:21
The renaissance of natural fibers: God's Forgotten Gift
By: Dr. Ahmed Hassanin
Co-Founder of InTEXive Consulting
info@intexive.com - www.intexive.com - http://www.palmfil.com
Once upon a time all materials were naturally based sources. There was only natural fibers but now that natural fibers have lost a lot of their market shares to synthetic fibers. As we mentioned in a previous article for Dr Midani (Reversing the shift back to natural fibers, https://fiberjournal.com/reversing-the-shift-back-to-natural-fibers/) that shifting back to natural fibers, become necessary.
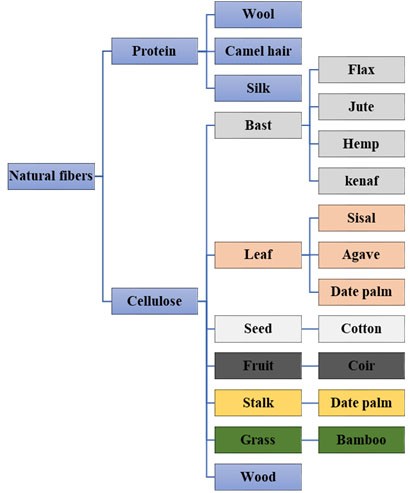
Natural fibers are fibers obtained from natural sources which could either be protein or cellulosic fibers. Protein or animal fibers are mostly obtained from animals while cellulosic fibers are obtained from plants. Cellulose natural fibers consist of three main organic constituents; cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
Usually cellulosic fibers are classified depending on the part of the plant from which they are extracted, for instance, fibers extracted from the stem are classified as bast fibers, whereas fibers extracted from the leaves are classified as leaf fibers. In addition to other parts of the plants, such as, seed, fruit, stalk, or grass as shown in Fig.1.
Natural fibers could be further classified into two types based on how they are found in nature. First, fibers that are present in fiber form. Second, fibers embedded in a natural matrix. The first type of fibers is used right away since the fibers are already found in fiber form, they don’t need further extraction, they may only require washing, drying then cutting such as cotton and wool. However, the second type of fibers requires further processing through many extraction or separation processes. These processes could be chemical, biological, or, mechanical. The extraction process is considered successful upon efficient extraction of the cellulose fibrils from the hemicellulose binding them and from within the lignin matrix in which they are embedded. Examples of these types of extracted fibers are flax, hemp, jute, sisal…etc.
Cellulosic Fibers
World Consumption of Cellulosic Fibers
Cellulosic fibers are the major natural materials used in the technical applications especially composites, Table 1. shows the world consumption of natural cellulosic fibers by type in values and quantities. Cotton fibers is excluded as it mainly used for textile applications. As it can be clearly noticed that Flax and Jute are the two most consumed natural fibers. Flax and Jute are used in many other applications rather than composites such as clothing, home textile and packaging materials.
Table 1 World consumption of vegetable fibers by fiber type in values and quantities
|
|
$US million |
|
103 tons |
||||
|
|
2010 |
2017 |
CAGR (%) |
|
2010 |
2017 |
CAGR (%) |
|
Flax |
1,641.0 |
1,963.2 |
2.6 |
|
427.8 |
455.0 |
0.9 |
|
Jute and other bast |
1,056.9 |
1,085.6 |
0.4 |
|
815.9 |
592.4 |
-4.5 |
|
Coconut |
306.4 |
543.1 |
8.5 |
|
672.5 |
1,080.1 |
7.0 |
|
Hemp |
10.9 |
16.3 |
5.8 |
|
13.2 |
20.0 |
6.1 |
|
Sisal |
5.8 |
8.2 |
5.1 |
|
5.7 |
4.0 |
-4.9 |
|
Other vegetable |
77.9 |
93.6 |
2.7 |
|
31.6 |
0.0 |
- |
|
Total |
3,100 |
3,700 |
2.6 |
|
2,000 |
2,200 |
1.3 |
As it can be obviously noticed from Table 2 that Flax prices is the highest among the other natural fibers. Jute come after Flax from the price point of view, this can be attributed to using these fibers in other high added value applications such as clothing and home textiles as mentioned earlier.
Table 2 Unit values of vegetable fibers in US$/Kg
|
|
$US/ Kg* |
||
|
|
2010 |
2017 |
CAGR (%) |
|
Flax |
3.8 |
4.3 |
1.7 |
|
Jute and other bast |
1.3 |
1.8 |
5.1 |
|
Coconut |
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.4 |
|
Hemp |
0.8 |
0.8 |
-0.2 |
|
Sisal |
1.0 |
2.0 |
10.4 |
|
Other vegetable |
2.5 |
0.0 |
- |
* Unit values (for each fiber) are average of fiber, yarn and fabric form
Asia pacific and Europe are the main regions consuming the natural fibers as indicted in Table 3. It is known that Asia Pacific countries are main producers for many natural cellulosic fibers such Jute, Kenaf, Coir, Kapok…. etc. While in Europe are the main producers of Flax fibers namely France, Belgium, Belarus and Ukraine.
Table 3 World consumption of Vegetable fibers by region in values
|
|
$US million |
||
|
|
2010 |
2017 |
CAGR (%) |
|
Asia Pacific |
1,244.4 |
1,825.7 |
5.6 |
|
Europe |
1,110.6 |
1,028.6 |
-1.1 |
|
Middle East |
447.3 |
460.0 |
0.4 |
|
North America |
228.0 |
299.3 |
4.0 |
|
Africa |
162.3 |
168.3 |
0.5 |
|
South America |
64.2 |
48.0 |
-4.1 |
|
World |
3,270 |
3,830 |
2.3 |
In our next series of articles, we will discuss in details examples of the most important natural fibers in our daily life such as cotton, flax, jute, wool…etc.